April 2020
By: Bryan Reynolds | 30 April, 2020

Amazon Web Services (AWS) is an on-demand cloud computing platform with customers that include organizations, individuals and governments. It consists of many services that collectively provide the tools and building blocks users need to develop their cloud infrastructure. Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is one of the most essential AWS services, since it provides users with computer resources via a cluster of virtual machines (VMs). These resources include central processing units (CPUs), storage, memory and networking capability. AWS VMs also include a choice of operating systems (OSs) and preloaded application software.
Read MoreBy: Bryan Reynolds | 25 April, 2020
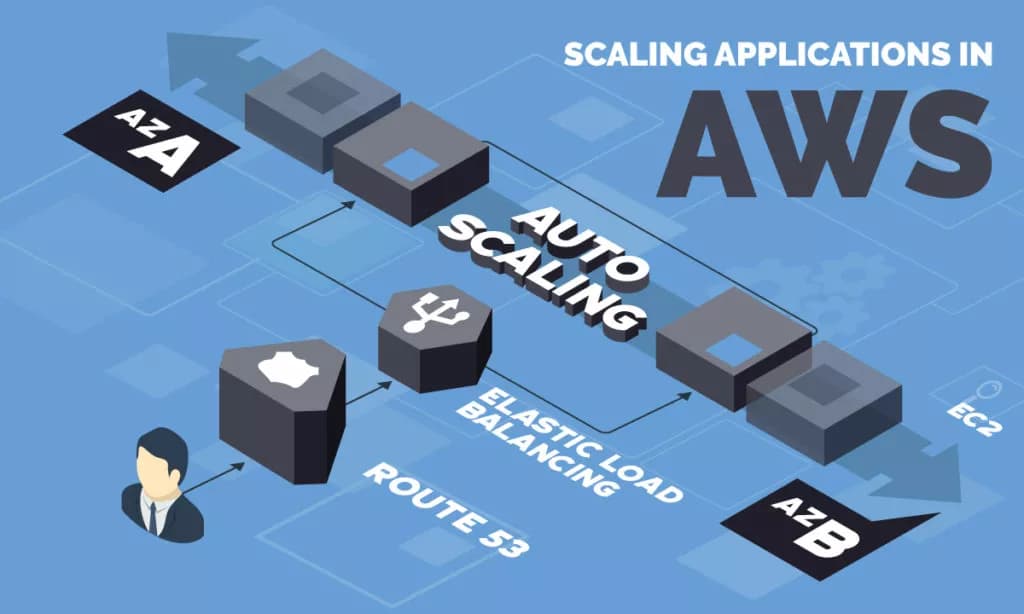
Cloud platforms typically provide users with access to virtual machines (VMs), rather than physical servers. This architecture allows the platform to quickly allocate computer resources such as storage, memory, and processing capability based on demand. Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a particularly large number of ways for users to configuring scaling on their platform, allowing them to find the best balance between cost and available resources. The scaling options available on AWS make it advisable for users to first develop an overall strategy before configuring their environment.
Read MoreBy: Bryan Reynolds | 14 April, 2020

The defining characteristic of cloud computing is the allocation of computing resources on-demand without direct management by the user. Data storage and computing power are the common resources allocated in cloud computing, although it can distribute any such resources to its users. The most common implementation of cloud computing is a data center that distributes resources to many users over the internet. The large platforms that now dominate the cloud-computing landscape typically have multiple servers that are geographically separated. In cases where the distance between the server and users is relatively small, the architecture may also be known as edge computing.
Read MoreBy: Bryan Reynolds | 31 March, 2020

A web application framework (WAF), also known as a web framework (WF), supports the development of web applications, which includes web application programming interfaces (APIs), web resources, and web services. Web application frameworks standardize the approaches developers use to build and implement web applications, largely by automating everyday tasks. For example, they often include libraries of routines that perform tasks like database access, session management, and creating framework templates. This routine helps promote the reuse of code, which reduces development time.
Read More

